Introduction
Drupal 7, launched over a decade ago, remains a cornerstone for 42.2% of websites using Drupal. However, with its End Of Life (EOL) scheduled for January 5, 2025, the platform will cease receiving essential security updates and bug fixes.
Why Drupal 7 EOL Matters
As the EOL date for Drupal 7 approaches, organizations relying on this robust CMS face critical decisions:
- Stay on Drupal 7 with Long-Term Support (LTS):
- Some organizations opt to continue with Drupal 7 by engaging long-term support providers. This option ensures continued stability while mitigating immediate migration costs.
- Upgrade to Drupal 10:
- Transitioning to Drupal 10 offers enhanced security, performance improvements, and access to new features. It represents a strategic investment in long-term digital infrastructure.
- Consider Alternatives:
-
- Organizations may explore migrating to alternative CMS platforms that better align with evolving business needs and technological advancements.

Choosing the Right Path Forward
Navigating Drupal 7's EOL requires a thoughtful approach tailored to your organization’s unique requirements. In the subsequent sections, we’ll delve into each option, providing insights to help you make an informed decision.
Option 1: Staying On Drupal 7
Drupal 7 will be supported until January 5, 2025. Post-EOL, approved vendors will provide security updates for Drupal 7 core and select modules through the Drupal 7 Vendor Extended Support program. This option is suitable for organizations needing time to prepare for migration or a CMS switch. However, prolonged use may lead to outdated modules and missed innovations. It's crucial for organizations to understand the implications of Drupal 7 EOL and plan accordingly.
Choosing to stick with Drupal 7 after its EOL is recommended for organizations needing more time to gather the resources required to upgrade or switch to a different CMS. Organizations must remember that this is a temporary solution, as with time, modules and integrations may stop working.
Websites stuck on Drupal 7 will also miss out on innovative new features. Because of this, organizations must be aware of answers to questions like 'When is Drupal 7 end of life releasing?' and 'What to do next?'
Option 2: Upgrading From Drupal 7 To Drupal 10
Upgrading to Drupal 10 or 11 offers significant advantages, including enhanced security, improved user experience, better performance, and superior mobile compatibility:
Enhanced Security:
Both Drupal 10 and 11 ensure ongoing security updates, which will be crucial post-Drupal 7 EOL.
Improved User Experience:
Enhanced UI/UX with modern frontend techniques and accessibility compliance.
Better Performance:
Faster page loads and scalability with a redesigned caching framework and updated PHP/Symfony dependencies.
Superior Mobile Experience:
Responsive design and modern web technologies ensure optimal performance on mobile devices.
Exploring more of Drupal 11's features can provide deeper insights into its capabilities and benefits.
Option 3: Migrating From Drupal To Other Platforms
Migration presents cost-effective opportunities depending on the website's needs:
- Platform Flexibility: Evaluate alternatives like WordPress, Contentful, or headless CMS solutions.
- Implementation Strategy: Plan meticulously to ensure a smooth transition, considering factors such as budget, objectives, and resource availability.
- Brand Enhancement: Leverage migration as an opportunity to refresh brand identity and improve website functionality.
Careful planning mitigates risks associated with migration expenses and ensures a seamless transition to a new platform.
Unlock the full potential of Drupal with expert migration, upgrade, and support services tailored to your organization's needs. Explore Drupal Services or Schedule a Consultation
Drupal To WordPress
Migrating from Drupal to WordPress is a good option for organizations that have plans to modify how their website is used. Switching to WordPress can be advantageous when organizations primarily require a user-friendly CMS and a website for ecommerce rather than just content.
But this migration can be complex without the right tools and techniques. The steps for carrying out a successful migration from Drupal 7 to WordPress are:
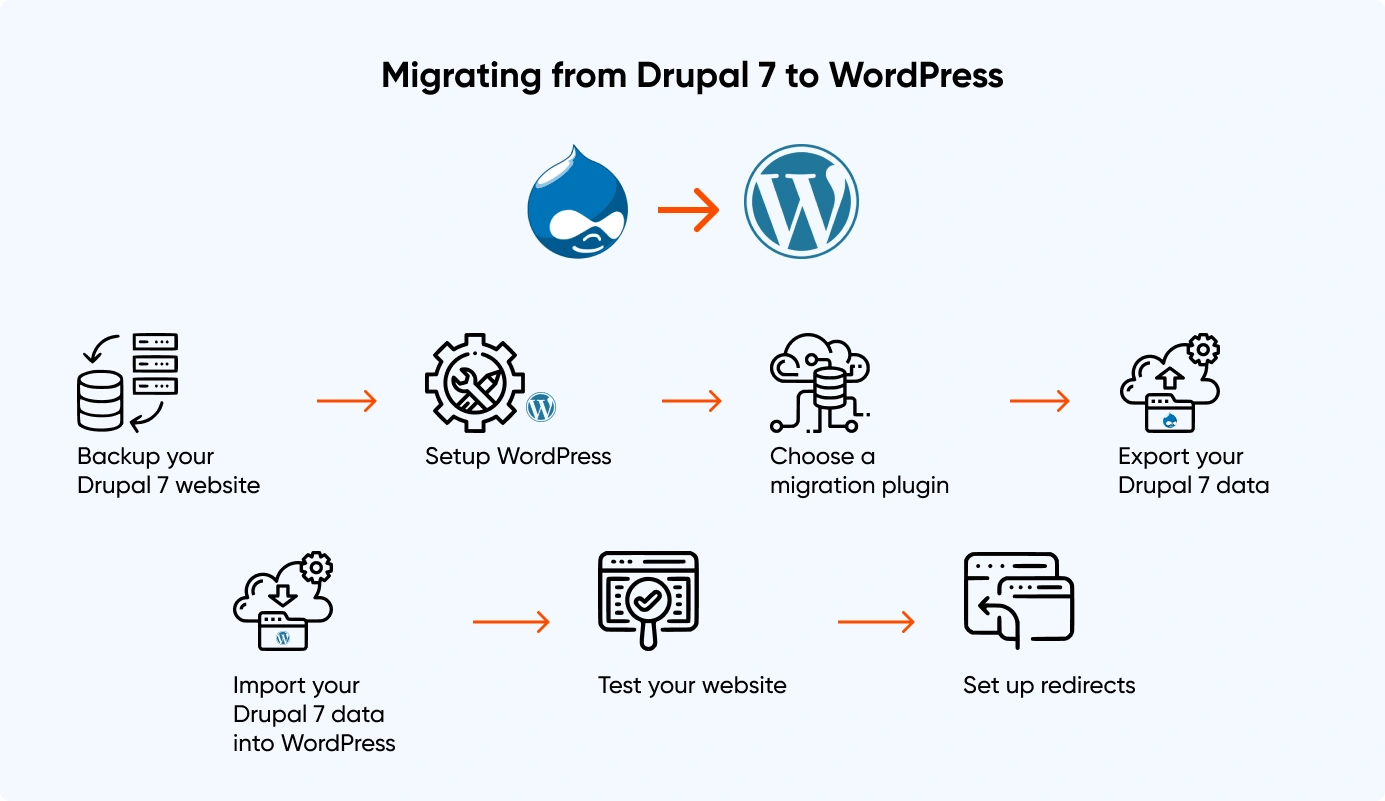
Back Up Drupal 7 Website
Before making any changes, it's important to back up the entire Drupal 7 website, including the database and files. The backup would be handy if one wishes to revert to Drupal 7. It will also act as a baseline for content migration.
Set Up WordPress
WordPress must be installed on a web hosting account. This can be done manually or using a one-click installer like Softaculous. For sophisticated websites, it is recommended to construct the website in a local development environment before hosting it.
Choose A Migration Plugin
Content can be transferred from Drupal 7 to WordPress by using a variety of plugins, including FG Drupal to WordPress and CMS2CMS plugins. Start by preparing a map between the source, Drupal 7, and the target, WordPress. If the migration is difficult, set up the necessary post types and taxonomies on the WordPress websites.
Export Drupal 7 Data
Export Drupal 7 data, including pages, posts, and media, into a format that can be imported into WordPress. The migration plugin selected during the previous step will typically have instructions on how to do this.
Import Drupal 7 Data Into WordPress
Next, import Drupal 7 data into WordPress using the migration plugin. The plugin will map Drupal 7 data to the appropriate WordPress fields and create the appropriate WordPress pages and posts.
Test The Website
Once the migration is complete, test the website to ensure that content has been transferred correctly and everything works properly.
Set Up Redirects
After migrating from Drupal 7 to WordPress, set up redirects to ensure old URLs point to the correct pages on the new WordPress website.
Going Headless
Developing a Headless application using Drupal consists of Drupal as a backend CMS for managing and storing content and a separate frontend framework like React or Angular to build the user interface. Converting an existing Drupal 7 website to a headless application will upgrade the website’s user experience to a new level.
Here's an overview of how a headless application can be developed using Drupal.
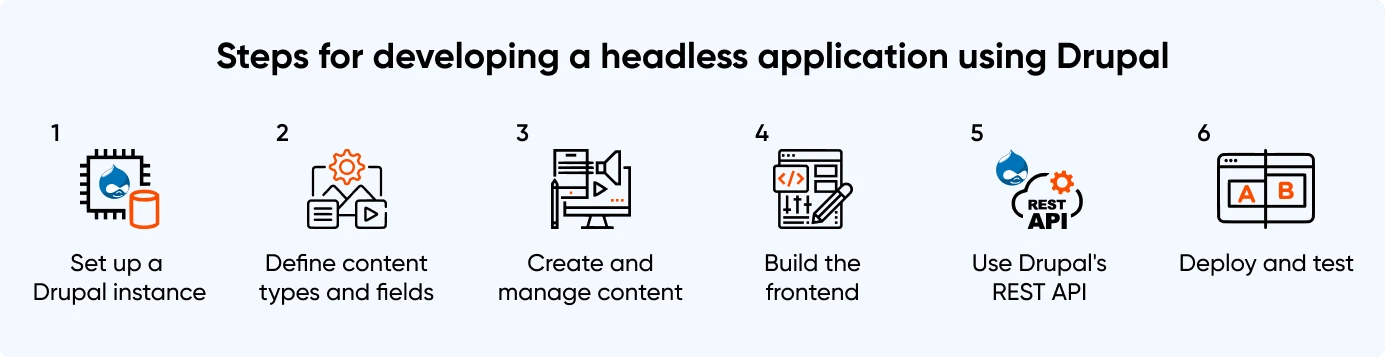
Set Up A Drupal Instance
Set up a Drupal instance to serve as the backend CMS for the headless application. This can be done on a personal server or using a Drupal hosting service.
Define Content Types And Fields
In Drupal, define the content types and fields that will store data. For example, there might be a content type for ‘articles’ with fields for ‘title,’ ‘body,’ and ‘image.’
Create And Manage Content
Once content types and fields are defined, start creating and managing content in Drupal.
Build The Frontend
The frontend of a headless application can be built using frameworks like React or Angular. The frontend will make API requests to Drupal to retrieve and render the content for users.
Use Drupal's REST API
Drupal includes a REST API that allows organizations to retrieve and manipulate content stored in Drupal. Using the REST API in the frontend code is recommended to retrieve content from Drupal and display it in the application.
Deploy And Test
Once the frontend is developed and integrated with Drupal, deploy the headless application and test it to ensure it works as expected.
Not Ready to Migrate from Drupal 7? Discover Our Drupal 7 Extended Support Options to Keep Your Site Secure and Up-to-Date!
Migrating To Contentful
Migrating from Drupal 7 to Contentful involves moving content from Drupal 7 to the Contentful CMS. Here are the steps to carry out this migration.
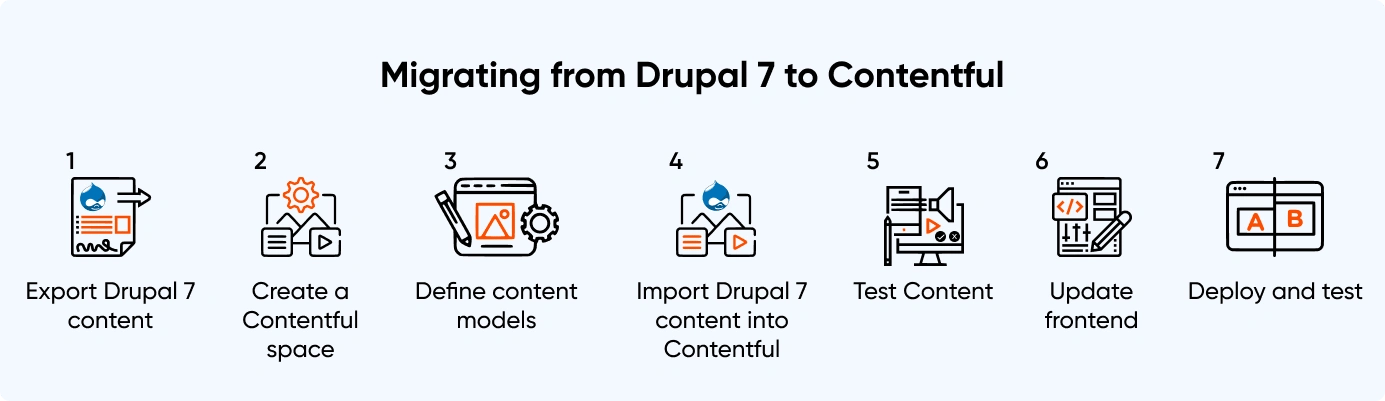
Export Drupal 7 Content
Export Drupal 7 content into a format that can be imported into Contentful. This can typically be done using a Drupal module such as Views Data Export.
Create A Contentful Space
Create a Contentful space to store content.
Define Content Models
In Contentful, define content models that match Drupal 7 content types. These models will define the content fields, such as text and image fields.
Import Drupal 7 Content Into Contentful
Once Drupal 7 content is exported, and a Contentful space is created, import content into Contentful using the Contentful CLI or the Contentful API.
Test Content
After content has been imported, test it in Contentful to ensure everything has been transferred correctly.
Update Frontend
If a frontend framework like React or Angular displays content, ensure the code is updated to retrieve content from Contentful instead of Drupal 7.
Deploy And Test
Next, deploy the new headless application and test it to ensure it works as expected.
Conclusion
Any of these three options can make sense depending on an organization's requirements. For example, organizations that need more time to gather resources should stick with Drupal 7 by opting for additional support while creating a migration or upgrade plan.
Alternatively, those looking to leverage the latest functionalities should consider upgrading to Drupal 10. Meanwhile, organizations seeking more user-friendly alternatives may explore migration to platforms like WordPress, Contentful, or headless solutions. If you're interested in learning more about migration options, feel free to explore our Drupal migration services.
Are you still unsure about what would work best for you?
The experts at Axelerant can help. Schedule a call to learn more.
FAQ'S

Gaurav Kapoor, Senior Drupal Engineer
Gaurav is a storyteller. An Arsenal FC fan, he also enjoys reading Amish Tripathi's works on Hindu Mythology. He has been spending every Friday evening at his favorite bar for more than two years now. Need a dose of sarcasm? He is your guy!

 We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.



Leave us a comment