Introduction
In 2023, Tesla’s vehicle deliveries grew 38% YoY to 1.81 million while production grew 35% YoY to 1.85 million. The car making company’s success has been shaped by its design thinking approach, built on several key principles:
- Customer-Centricity: Tesla recognized the growing demand for more affordable electric vehicles but identified gaps in the market offerings. The Model 3 targeted a lower price point than previous Tesla models,making it more accessible to a wider audience. Over 400,000 pre-orders for the Model 3 soon after its unveiling, showcases significant customer demand for a more affordable electric car.
- Rapid Prototyping And Iteration: Rapid prototyping allows for quick testing of concepts with users, ensuring solutions address their actual needs and desires. Rapid prototyping enables early identification of flaws, minimizing wasted time and resources on solutions that don't resonate with users.
- Tech-Meets-Design: Over two million Tesla vehicles globally equipped with Autopilot displays the integration of technology and design. This also demonstrates customer interest in advanced driver-assistance features, showcasing Tesla's ability to blend cutting-edge technology seamlessly into its vehicle designs.
It's evident from Tesla's example that design thinking is more of a mindset and approach to problem-solving and innovation.
What is Design Thinking?
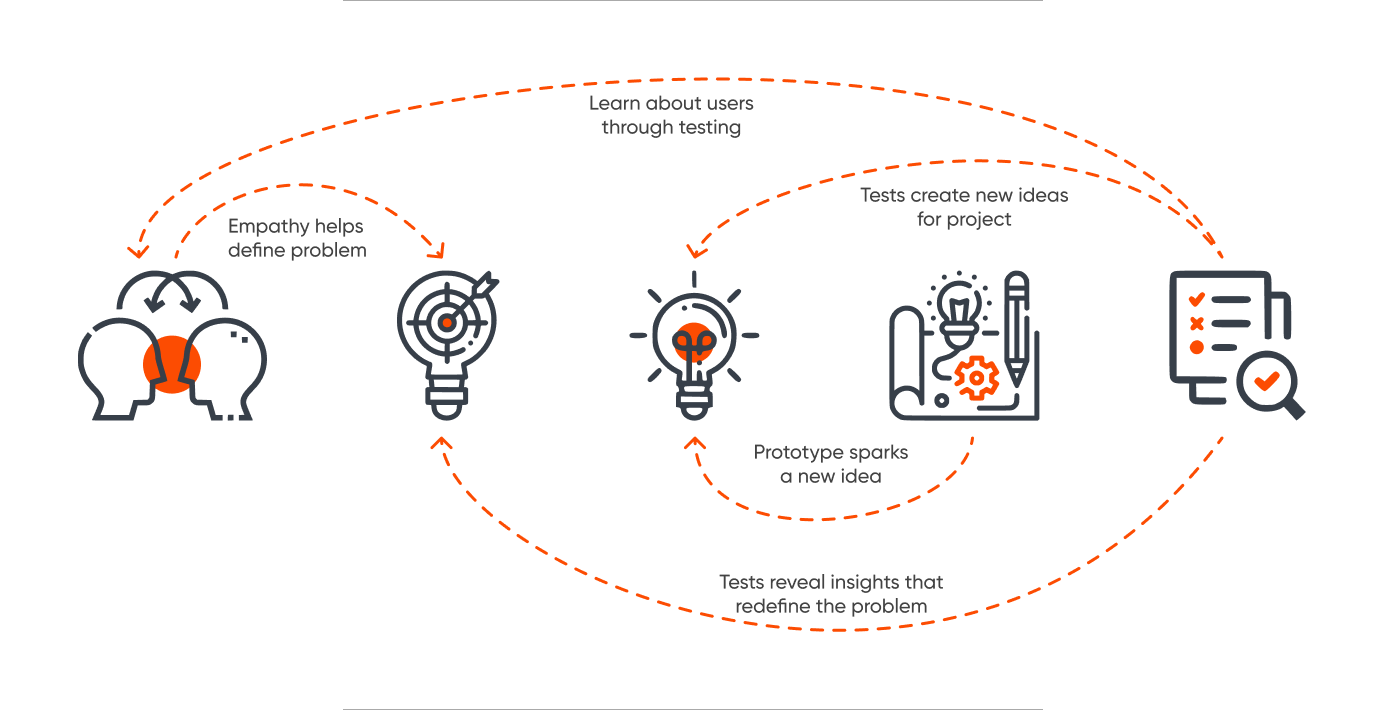
According to the Interaction Design Foundation, design thinking meaning is explained as follows:
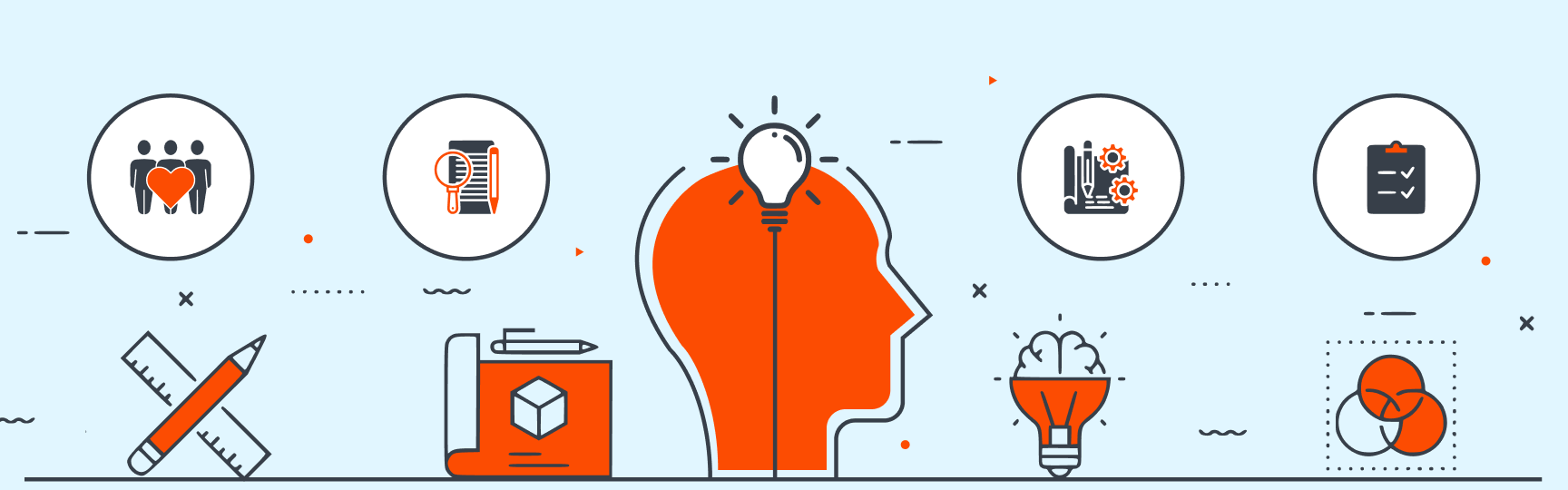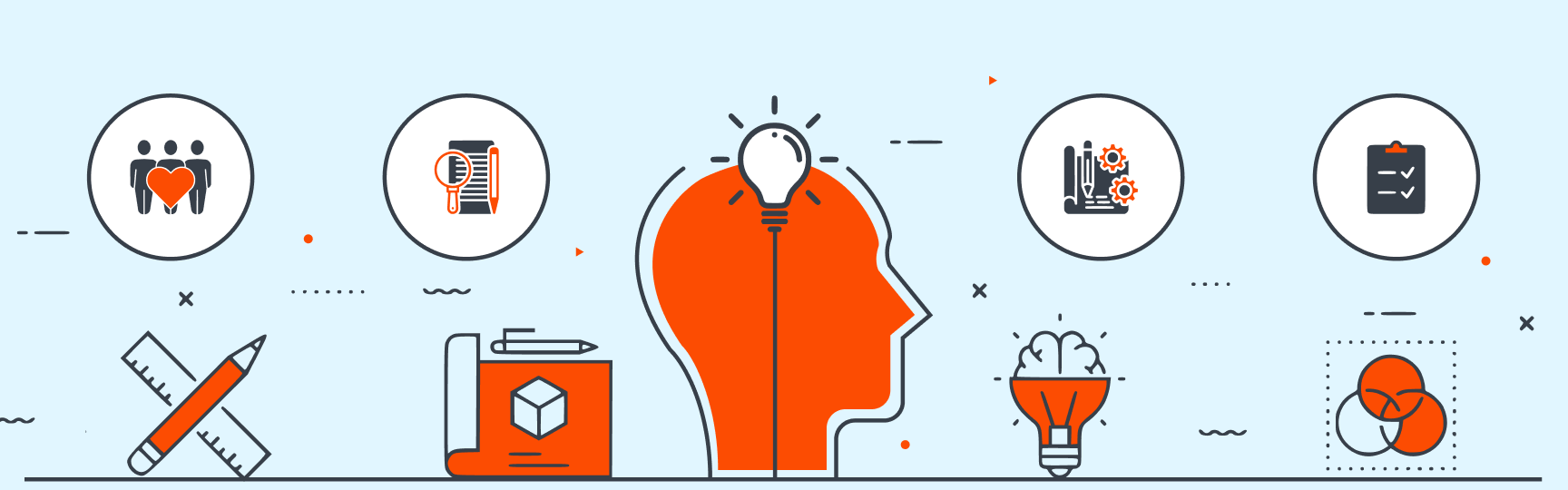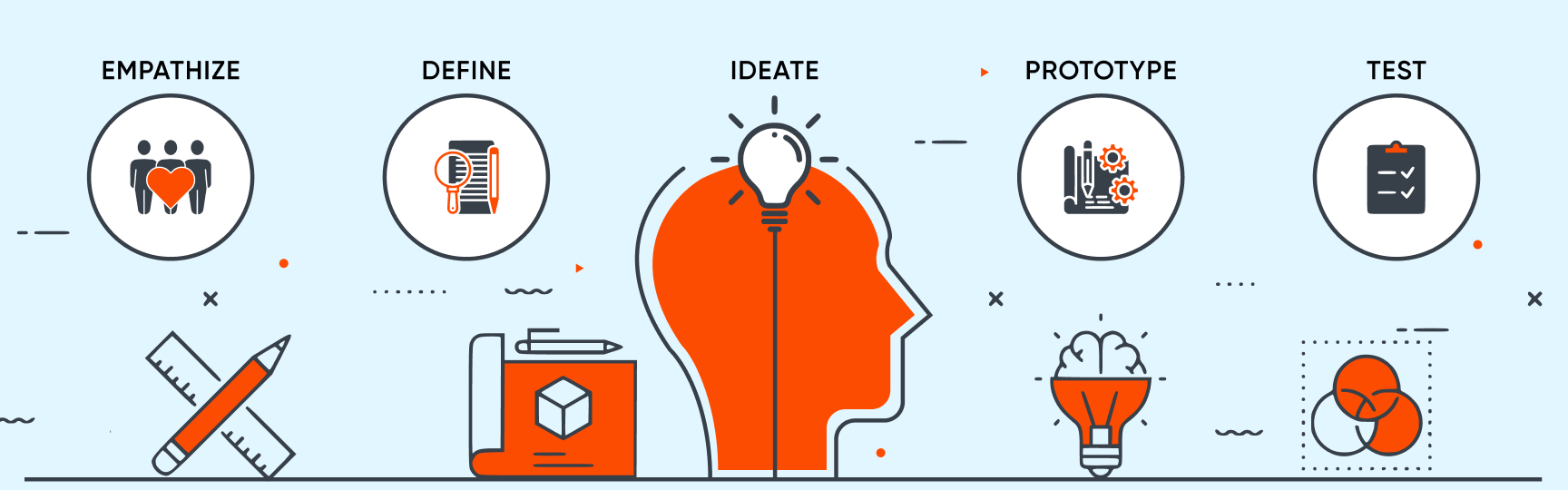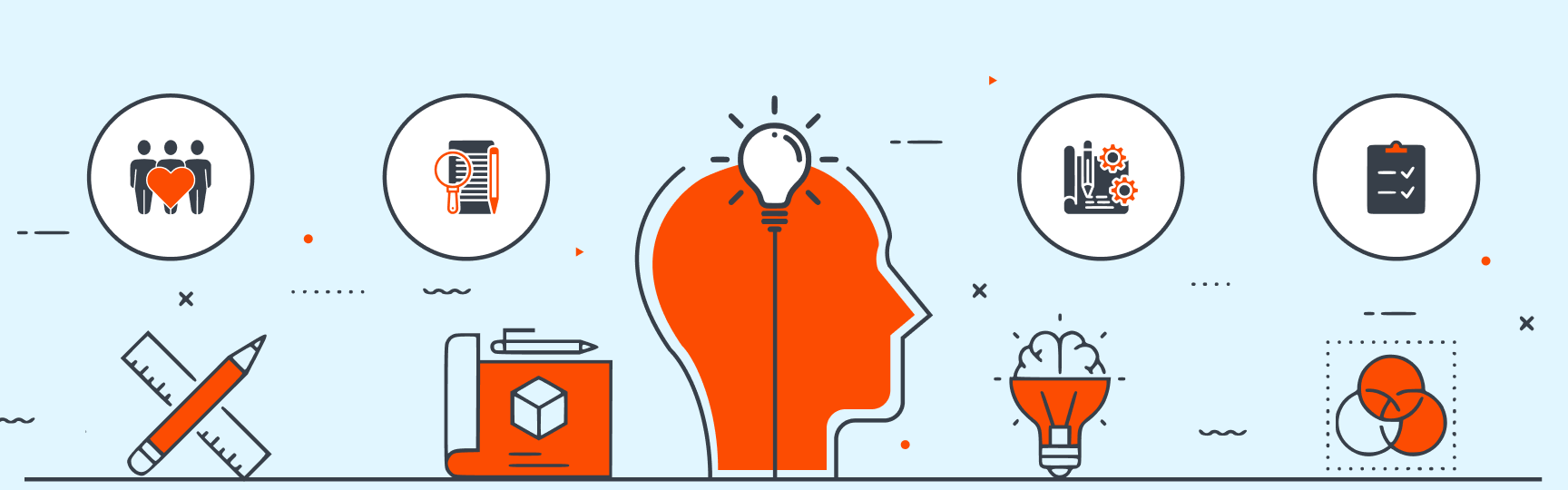
Design thinking methodology is a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. It is most useful to tackle ill-defined or unknown problems and involves five phases: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test.
- Empathize: Gain a deep understanding of end users, their challenges, and expectations through observation, interviews, and surveys. This immersion helps design teams grasp the problems to solve effectively.
- Define: Craft a clear problem statement with a measurable goal that aligns with user needs. Through collaboration with stakeholders, refine the statement until everyone agrees on the precise challenge to address.
- Ideate: Generate diverse ideas to tackle the defined problem using brainstorming and other ideation techniques. Collaborate with stakeholders to explore innovative solutions.
- Prototype: Create testable prototypes or scaled-down versions of the product, collaborating with stakeholders to select promising concepts. Utilize various prototyping tools, from simple paper models to interactive digital prototypes.
- Test: Evaluate the prototype's effectiveness with target users, gathering feedback to refine and improve the solution before further development or implementation. Conduct testing sessions to observe user interactions, collect feedback, and analyze usability data.
Design Thinking In Action: How Airbnb Achieved It
Airbnb immersed themselves in the lives of their potential customers by visiting New York, renting a camera, and spending time with people in their homes to capture quality pictures.
This process, driven solely by intuition and lacking preliminary studies, wasn't scalable or highly technical, but it proved effective to understand the brand’s target audience.
The team diverged from traditional business methods, opting instead to follow the steps of the design thinking methodology: empathize, define, design, prototype, and test.
Today, design thinking remains ingrained in Airbnb's culture, influencing their creative processes, product iteration, and community engagement. Its design system initiative resulted in a cohesive set of design components and tools for improved team collaboration.
Airbnb has seen exponential growth, revolutionizing the tourism industry and achieving a valuation of $110 billion. With over 1 billion stays booked and millions of listings worldwide, their impact is visible.
Lessons from Airbnb’s Design Thinking process:
- Prioritize human experience: Ground your work in real human behaviors and needs to build trust and create desirable products.
- Embrace experimentation and iteration: Proactively test creative hypotheses and adapt based on feedback, without being solely driven by data.
- Take calculated risks: Encourage team members to make small bets on new features and learn from both successes and failures.
What Are The Advantages of Design Thinking?
Design thinking in software development includes a creative approach to problem-solving that is focused on the users. Various industries have understood why design thinking is important. Mckinsey reported that companies that score highest in its Design Index (MDI) outperformed industry-benchmark growth by as much as two to one.
Here are the benefits of design thinking:
 Promotes Customer-Centricity
Promotes Customer-Centricity
Prioritizes customer needs and preferences, leading to the development of products and services tailored to user requirements.
 Enhances Agility & Adaptability
Enhances Agility & Adaptability
Encourages creative exploration and experimentation within the organization, driving the development of innovative solutions.
 Fosters A Culture Of Innovation
Fosters A Culture Of Innovation
Leads to creative experimentation, driving the development of novel solutions.
 Improved Problem Solving
Improved Problem Solving
Equips teams to identify, address, and overcome challenges, leading to innovative problem-solving approaches.
 Business Integration
Business Integration
Seamlessly integrates design thinking into organizational processes, facilitating alignment with strategic goals.
 Enhanced Product Usability &Acceptance Rate
Enhanced Product Usability &Acceptance Rate
Helps develop intuitive, easy-to-use products that meet user expectations, leading to higher adoption rates.
 Resource Optimisation
Resource Optimisation
Streamlines the innovation process by minimizing unnecessary steps and focusing on what truly matters, saving resources.
 Tangible Results
Tangible Results
Empowers teams to achieve user-centric results, leading to a more engaged workforce and higher productivity.
Challenges Of Implementing Design Thinking
While design thinking offers numerous benefits, its implementation comes with a set of challenges requiring organizations to navigate potential obstacles to maximize its effectiveness.
- Resistance To Change: Organizations may face resistance to change, especially if the existing culture prioritizes traditional, non-collaborative approaches. Overcoming this resistance requires strong leadership commitment and communication.
- Resource Crunch: The design thinking process demands significant time, effort, and resources, posing challenges for organizations with tight schedules or limited budgets. Balancing the investment with expected returns becomes crucial.
- Lack Of Skills: Design thinking requires a specific skill set that may not be readily available within the organization. Hiring or training employees proficient in design thinking methodologies becomes essential but can be challenging.
- Ambiguity: Design thinking embraces ambiguity and iteration, which can be unsettling for organizations seeking concrete, predictable outcomes. This uncertainty may lead to discomfort among stakeholders.
- Inadequate Integration with Business Processes: Failure to seamlessly integrate design thinking into experience design or business processes may result in a disjointed approach. The challenge lies in aligning design thinking with broader organizational strategies and structures.
- Overemphasis on Empathy: While empathy is a cornerstone of design thinking, an overemphasis on it may lead to solutions that are overly subjective. Striking a balance between empathy and objective analysis is crucial for effective problem-solving.
- Difficulty in Scaling: Successfully implementing design thinking in a small team does not guarantee scalable success across the entire organization. Scaling up requires careful planning and may encounter resistance at different levels.
- Measuring Impact: Quantifying the impact of design thinking in terms of ROI can be challenging. The outcomes are often qualitative, making it difficult to measure success in traditional business metrics.
Conclusion
There are many ways to approach problem-solving and innovation. Design thinking is just one of them. While it’s beneficial to learn how others have approached problems and evaluate if you have the same tools at your disposal, it can be more important to chart your own course to deliver what users and customers truly need.
Want your business challenges solved by design thinking in action? Learn more by speaking with an expert.
FAQ'S
The five steps that make up the design thinking overview: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. By now, you've probably heard about the design thinking methodology.
The goal of the customer design thinking process is to come up with solutions, products, or services that are desirable for the user, economically viable from a business perspective, and technologically feasible.
Design thinking is a problem-solving skill.
Design thinking meaning: It is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and experimentation to generate innovative solutions.
Businesses are built for people.
Business design thinking helps understand what the people need, want, and feel. It's not just about making cool products, it's about creating solutions that truly matter to your customers, employees, and partners.
The business value of design is obvious from a quick statistic.
PepsiCo CEO Indra Nooyi stated that design had a voice in almost every crucial decision the company made. During her 12 year tenure, sales increased 80 percent.

Dheeraj Khindri, Director of Experience Design
A pragmatic soul and cinema enthusiast who enjoys larger-than-life films—that’s Dheeraj. In his free time, he explores all things poetry, solo guitar sessions, and binge-worthy web series. His life’s essential values? Empathy, autonomy, and pragmatism.

Sucheta Biswas, Marketing Coordinator
Nicknamed “Monica” for her culinary prowess and tidiness, Sucheta is an intriguing omnivert. Books are her cherished companions, complemented by nature walks and wildlife photography. She’s also a practicing Yogi who loves all things art.
 We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.


Leave us a comment